Entrepreneurs worldwide are asking: “How can these companies sell so cheaply?” The answer is more complex than just cheap labor or massive factories. It’s a digital, financial, and data-driven ecosystem designed for market domination.
Here are the key factors that allow them to sustain seemingly impossible prices, and the risks this poses for everyone.
1. The Market Subsidy Model: Losing Today to Win Tomorrow
The main strategy of these platforms is market subsidization, an aggressive practice where they intentionally sell key products below their actual cost.
- How does it work? If a product costs $8 USD to produce and ship, they might sell it for $5 USD. They lose $3 USD per unit, but they do this deliberately and sustainably for years.
- The real goal: These losses are funded by a massive capital from investment funds and credit lines, allowing them to attract millions of customers quickly, create a buying habit, and crush local competition before it can grow. It’s a long-term investment to control the market.
- The “Kill Zone” strategy: If a strong local competitor appears, these platforms will lower their prices even further in that region to suffocate the newcomer, using their enormous financial backing to outlast any new player.
2. From Losses to Profits: The Real Business Is Beyond the Products
This is the crucial point that sets them apart. While they lose money on one side, they earn and multiply it on another, creating an unstoppable “snowball effect.”
- Massive advertising and coupons: They spent over $1 billion in advertising in the U.S. alone in their first year, along with coupons, giveaways, and sweepstakes. It’s a huge expense, but it lets them capture millions of customers at a record pace.
- The real treasure: Your data. Every click, purchase, search, size, and preference you share becomes valuable information. This data is used for:
- Hyper-personalization: They show you products with incredible accuracy to maximize your purchases.
- Hidden monetization: Aggregated data becomes a valuable database that can be used to generate revenue in sectors like marketing, insurance, or banking.
- The “snowball effect”: They spend heavily at the beginning to attract a large volume of customers. Once a customer is in, they spend less on advertising to retain them. A percentage of those initial customers become repeat buyers, and over time, their business becomes profitable.
3. Total Supply Chain and Global Logistics Control
Their dominance over the entire supply chain gives them an advantage that most businesses simply cannot match.
- Economies of scale: They purchase millions of meters of fabric, chips, or components per year, reducing the cost per unit to a minimum.
- Optimized logistics: They negotiate massive discounts on sea and air freight that a regular company could never get.
- Supplier dominance: They control everything from design to production and delivery. Suppliers depend so heavily on them that the company can shift production in a matter of days without prices being affected.
4. Geopolitical and Logistics Strategy: The Case of the Port of Chancay
The ability of these platforms to dominate markets extends beyond their own businesses; it is supported by strategic commercial planning. A clear example of this is the multi-billion dollar investment in the Port of Chancay in Peru.
This investment is not charity, but a move to secure and improve the maritime route to South America, significantly reducing transit times and shipping costs for the entire region. Their strategic logistical control allows low-cost shopping companies to maintain a competitive edge. , flooding Latin American markets with low-priced products. For them, this infrastructure isn’t just a port; it’s a key piece to secure control of a massive market and a way to recover their investment through a constant flow of goods.
5. The Risks for Your Wallet and Your Community
These low prices come with a hidden cost that, in the long run, affects you, your family, and your community.
- Destruction of local industry: Local businesses—whether in textiles, technology, or agriculture—cannot compete and are forced to close, eliminating jobs and trades in your region.
- Quality and planned obsolescence: Products, often of low quality and designed for a short lifespan, promote a disposable culture that is harmful to the environment and forces you to buy more often.
- Privacy risks: Your personal and financial information may end up in the hands of third parties without your consent, as privacy policies are not always clear or transparent.
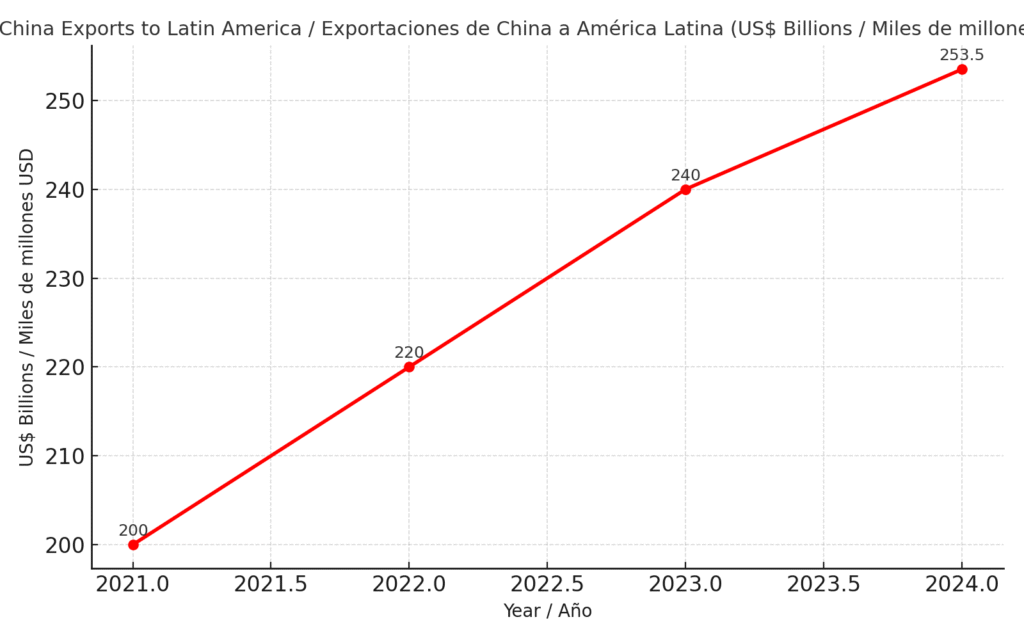
| Year | China Exports to LATAM (US$ bn) | Job Loss in Manufacturing (thousands) | Industries Affected |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 200 | 150 | Textiles, footwear |
| 2022 | 220 | 210 | Electronics, furniture |
| 2023 | 240 | 280 | Steel, auto parts, appliances |
| 2024 | 253.5 | 320 | Ceramics, apparel, plastics |
The surge in Chinese exports to Latin America isn’t just an economic trend—it has coincided with significant industrial challenges in the region. Data and business reports reveal a clear pattern of consequences.
Massive Import Growth: China’s exports to Latin America have soared to approximately $275 billion in 2024, creating trade imbalances across the region.
Manufacturing Collapse: This import boom has correlated with a sharp drop in local manufacturing jobs. Cheap products have led to layoffs and factory closures. For example:
In 2023–2024, two major steel plants in Chile and Brazil closed amid rising import competition, affecting hundreds of thousands of jobs.
Mexico lost nearly a million manufacturing jobs in the 2000s, and its textile industry shed roughly 450,000 jobs over 15 years, largely due to increased competition from low-cost imports.
- Hardest-Hit Sectors: The most affected industries include steel, textiles, electronics, autoparts, and home appliances. These sectors have been flooded with low-cost goods, forcing numerous local workshops and factories to shut down.
6. What Future Are You Building with Your Purchases?
The closing of markets in the U.S. and the E.U. makes Latin America the new target. And here is where the choice is yours.
By supporting this model, not only are local businesses threatened, but it also suppresses innovation and access to quality technology. To cut costs, quality control is often skipped, sometimes exposing your health to risks.
The taxes that are no longer paid due to local business failures mean that public services worsen, investment in education and healthcare stagnates, and corruption increases. The scarcity of skilled jobs becomes the norm, and your quality of life declines over the years.
The real savings don’t exist. Your wallet might feel a small advantage today, but the consequences of this market destruction will be far more expensive for you and future generations. Are we really building a better future for our children this way?

